Record Retention Guidelines Overview
Every organization battles mounting digital clutter while trying to stay on the right side of regulations. A clear set of record retention guidelines cuts through the noise, showing you exactly what to keep, where it lives and when it’s time to let it go.
A solid policy turns vague “maybe we should” conversations into firm decisions. Teams know when a document still has value and when it’s just taking up space—saving money and reducing audit stress.
- Define statutory retention periods based on industry regulations.
- Map record categories to owners, storage locations and system tags.
- Schedule regular reviews to adjust timelines and handle exceptions.
- Enforce secure destruction via certified services and a documented chain of custody.
The following infographic visualizes the journey from defining requirements to final disposal.
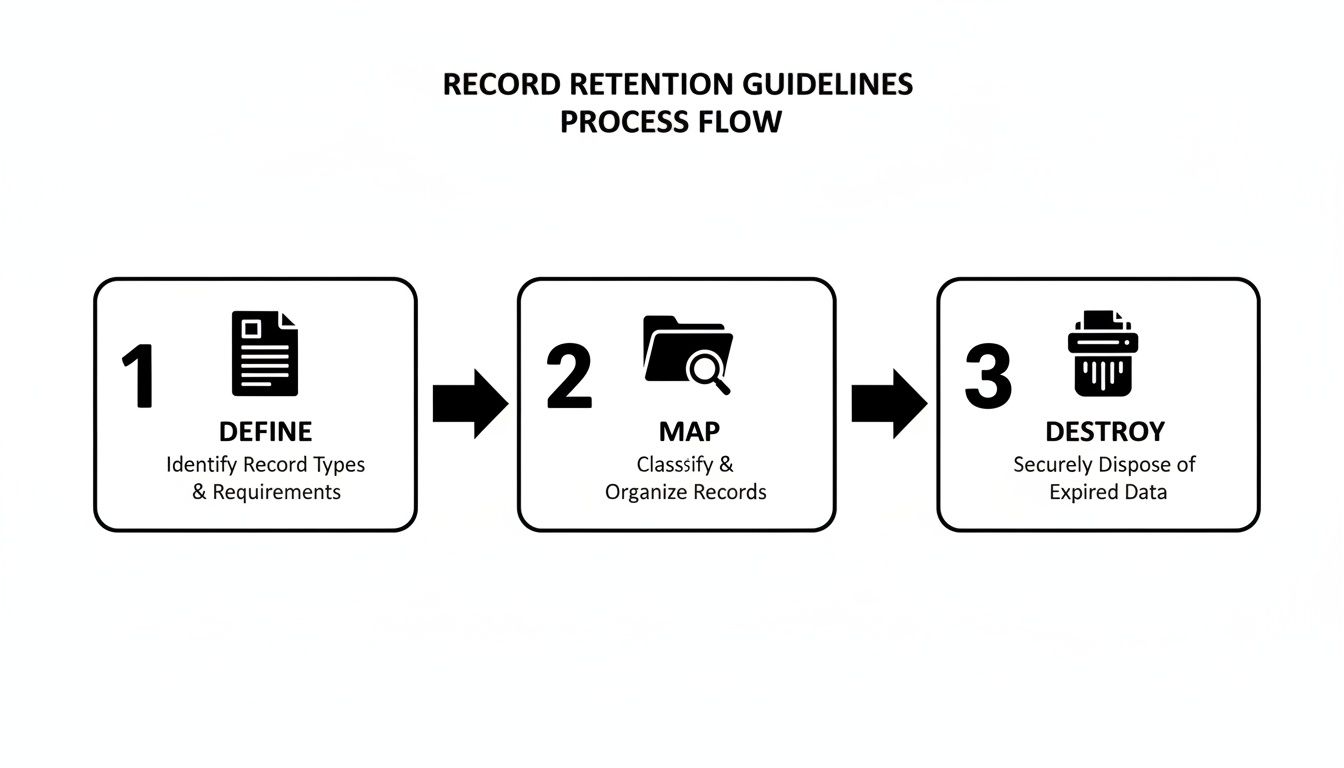
Retention Steps Overview
Below is a high-level snapshot of each phase in your retention framework, from policy creation to secure disposal.
| Phase | Key Action | Outcome |
|---|---|---|
| Define | Document legal and business requirements | Establish baseline retention periods |
| Map | Categorize records and assign responsibilities | Clear visibility into record types |
| Destroy | Securely dispose of records after retention ends | Reduced storage costs and compliance |
This table makes it easy to see who does what—and why—at each stage.
You might also explore our asset lifecycle management guide to connect record and asset governance.
Key Benefits You Need To Know
- Minimizes Legal Risk by matching retention periods to statutes of limitations.
- Cuts Storage Expenses through routine disposal of outdated records.
- Boosts Audit Defensibility with clear timelines and documentation.
- Enhances Data Governance by removing clutter and focusing on critical files.
These advantages turn your retention plan into a proactive tool—not just a compliance checkbox.
Phase Details
- Define Phase: Legal and compliance teams identify all relevant statutes and company requirements.
- Map Phase: Records are categorized, tied to department owners and tagged for easy retrieval.
- Destroy Phase: Certified vendors manage secure shredding or data wiping with full chain-of-custody logs.
- Review Triggers: Automated alerts flag documents that have reached their expiration, eliminating manual oversights.
Each step flows into the next, keeping you both agile and audit-ready.
Visualizing The Workflow
When you pair the infographic with the summary table, every team member can instantly see where each record stands. That clarity speeds up audits and helps reclaim valuable storage space.
Next Steps You Need To Know
- Assign a record custodian for each category and equip them with targeted training.
- Implement automated workflows to launch review cycles, disposition triggers and audit logs.
- Review the schedule annually or any time a regulation changes.
Understanding Record Retention Concepts
Picture your company’s data like a vast library—only instead of dusty books, you’re managing invoices, emails, contracts and HR files. Every piece of this collection is a business record, documenting company activity and triggering legal deadlines.
Regulations spell out exactly when a record moves from active use to locked storage or secure destruction. Having clear timelines not only strengthens your audit defensibility but also slashes redundant data costs by weeding out files you no longer need.
These rules also keep you in line with privacy laws like GDPR and HIPAA, protecting both your organization and the people whose data you hold.
- Tiered storage zones act like library shelves that shift documents from active to archive areas
- Retention clocks start the moment a file is created—flagging review dates like a library due date
- Audit trails work as checkout logs, recording every access, move and destruction step for legal proof
With this library analogy, you can see how records flow in and out of zones on a predictable schedule. That prevents backup bloat and eases audit headaches by ensuring nothing lingers past its lifecycle.
Tiered Archive Analogy
Think of a multi-level archive. On the ground floor, you find current invoices. Descend a level for older employee files. Go deeper still for sealed vaults holding expired legal records.
A retention clock marks milestones: at five years, a file moves deeper; at its legal end date, it’s purged.
Each tier has clear custodianship and event-driven actions. That structure makes your policy rock-solid during legal reviews and audits.
Clear, consistent retention rules turn tangled records into a well-oiled archival machine and provide audit-ready proof.
In practice, you label digital files with secure metadata tags and set automated alerts to handle each transition.
Key Benefits Explained
When retention rules are crystal clear:
- Audits run smoothly—teams aren’t scrambling for missing files.
- Storage costs shrink by purging obsolete data; experts estimate eliminating ROT can cut expenses by up to 30%.
- Governance strengthens through defined ownership and scheduled reviews.
These perks build confidence in your policy. Scheduled cleanups become routine, and your team trusts the system to manage risk and free up space.
This conceptual groundwork answers the “why” of retention before you dive into “how.” For example, a financial firm might set a seven-year clock on tax files and automate archive transitions.
The global record keeping system market was valued at approximately US$22.76 billion in 2025 and is forecast to reach US$52.88 billion by 2032, reflecting demand for compliant archiving and disposal capabilities. Learn more about these market findings on Coherent Market Insights.
You might also check out our guide on secure data disposal and cleansing to see how disposal complements retention. Read also our article on data sanitization.
With this foundation, you’re ready to build a schedule that aligns with laws, costs and business needs. This conceptual overview fuels the strategy for crafting precise retention schedules that balance risk and efficiency.
Common Retention Periods By Industry

Every sector has its own diary for how long records must stick around. Small businesses juggle legal timelines against tight storage budgets. Healthcare outfits answer to HIPAA’s calendar for patient charts and billing logs. Meanwhile, schools and government agencies often keep archives indefinitely unless a rule or a request pulls them down.
Typical Small Business Windows
Most small firms hang on to tax and financial documents for seven years to satisfy IRS audits. Employee files usually stay in storage for seven years after someone leaves, just in case a claim turns up later.
- Client contracts commonly live for five to ten years once a project wraps.
- Insurance policies and related paperwork often follow a six-year state-mandated window.
This lean approach frees up space without missing a legal beat. And as your company expands, scaling these timeframes is straightforward.
Healthcare Retention Requirements
Under HIPAA, medical records must remain accessible for at least six years from their creation date. In Georgia, certain files—think pediatric charts—stretch that requirement to ten years.
Key Insight: Proper retention isn’t just about avoiding fines; it’s about protecting patient privacy and trust.
- Check out our guide on the medical equipment recycling program for e-waste best practices alongside retention.
Education, Finance, And Government
Universities often archive transcripts and diplomas permanently—or until a graduate asks for removal. Financial firms, from brokerages to tax consultancies, must keep audit trails and tax paperwork for seven years under IRS and SEC rules. Government departments? They vary wildly. Defense and legal records sometimes demand decades of custody.
Here’s a side-by-side snapshot of standard retention across key sectors:
Industry Retention Period Comparison
| Record Type | Small Business | Healthcare | Education | Finance | Government |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Financial & Tax | 7 years | 6 years | 7 years | 7 years | Varies |
| Employee Records | 7 years post-termination | 6 years | 7 years | 7 years | Varies |
| Client Contracts | 5–10 years | 10 years | 5 years | 5–10 years | Varies |
| Transcripts & Diplomas | N/A | N/A | Permanent | N/A | N/A |
This table makes it clear that although seven years is the most common timeframe, certain sectors—especially education and government—require longer holds. You can dive deeper into these research findings at the TrueITPros data retention guide.
Statutes And Audit Triggers
Often, the statute of limitations for contract disputes sets that seven-year baseline. But if an audit knocks on your door, those records stay put until the investigation wraps up. Your policy should define these triggers clearly.
Local Atlanta Considerations
Georgia’s retention statutes largely mirror federal rules, but you’ll find quirks in healthcare and education regulations. If you’re operating in Metro Atlanta, make sure your schedule aligns with both state mandates and industry guidance to dodge local fines.
Local compliance starts with robust record lifecycles.
- Define clear triggers for each record category based on legal and business needs.
- Review retention schedules annually to account for law changes.
- Use metadata tags to automate archiving and deletion workflows.
- Train your team on retention policies to ensure consistent enforcement.
Key Takeaways
- Align retention windows with industry standards and Georgia statutes.
- Embed audit triggers to safeguard against unexpected legal gaps.
- Integrate secure destruction and recycling practices into your disposal phase.
Customize this framework for your sector, and you’ll build a defensible, cost-effective retention strategy. Start today.
Creating A Retention Schedule And Policy
Laying out your retention framework is a lot like plotting a roadmap—you need clear destinations. Begin by linking each record type to the department that relies on it.
For example, tuck financial reports under Accounting and align personnel files with Human Resources. This simple mapping keeps documents from floating in no-man’s-land.
Then, designate custodians who will shepherd each record from secure storage through periodic reviews all the way to disposal.
- Identify record categories and assign a dedicated owner.
- Map each category to applicable regulations, such as HIPAA or SOX.
- Set retention clocks that automatically trigger deletion once the timeframe lapses.
Don’t skip stakeholder interviews. A few targeted conversations with Legal, Compliance, and IT can surface unique needs your initial draft might miss.
Assign Roles And Approvals
Think of the policy owner as your project’s north star. This person champions updates, drives training, and maintains overall accountability.
Next, schedule a legal review meeting to iron out retention periods and carve out any necessary exceptions. That one session often clears up ambiguities that trip up organizations later.
“At one mid-sized firm, undefined disposal roles led to documents piling up for months. They ended up paying thousands in avoidable storage fees and scrambling to meet audit deadlines.”
The solution? Assign disposal tasks by role. Suddenly, everyone knew their part, and confusion vanished. Once roles are crystal clear, your system can fire disposition alerts the moment a record reaches its expiry date.
- Configure your document management software to tag items at creation with review and deletion dates.
- Run test cases to ensure alerts reach custodians before disposal.
- Build in a manual approval step for legal holds or special exceptions.
Even the smartest automation needs human oversight—schedule a formal policy review at least once a year, or any time regulations shift.
Training And Audit Procedures
Dense manuals don’t stick. Instead, deliver record retention guidelines for businesses in brief, role-specific workshops.
- Distribute quick-reference cards showing retention timelines and custodian contacts.
- Use real-world scenarios to highlight the impact of skipping steps.
- Reinforce learning with short quizzes or interactive demos.
To tie everything together, align your retention schedule with your hardware lifecycle controls. For more on that, explore our guide on IT Asset Management Best Practices.
Cap it off with regular audits: sample records, verify secure destruction logs, and flag any gaps. Maintain a central policy manual with version control to track updates, approval dates, and responsible stakeholders. Slip policy overview into your new-hire onboarding so everyone starts on the same page.
- Appoint a policy administrator to oversee annual reviews and legal changes.
- Archive superseded versions with clear labels to preserve your audit trail.
- Host quarterly check-ins with department heads to catch emerging needs promptly.
Conclusion And Next Steps
- Map each record type to a custodian for clear accountability.
- Define retention clocks and automate disposition alerts.
- Conduct annual policy reviews and quarterly department check-ins.
- Roll out role-based training with handy reference guides.
- Audit disposal logs and keep your policy manual current.
Ongoing engagement is the key to keeping retention policies alive.
Why wait? Begin drafting your retention schedule this week and seize control of your records.
Secure Destruction And E-Waste Disposal Practices

Imagine every record—whether on paper or a server—as a deposit tucked away in a high-security vault. When it’s time to clear space, you need more than a shredder or a delete key; you need a documented process that leaves no room for doubt.
Physical media and digital files left unattended can turn into liabilities. In fact, studies show nearly 70% of enterprise data holds no business, legal, or regulatory value, yet organizations keep it around, stacking up storage and compliance headaches.
Key Certified Destruction Methods
• Certified data destruction services that meet DoD standards
• Chain-of-custody logs for each handoff and transport
• Tamper-evident certificates proving every item was properly destroyed
These steps stitch together an audit trail you can trust: once it’s gone, it really is gone.
Case Study On Defensible Destruction
A small clinic in Alpharetta faced a scare when shredded tapes turned up missing. Their vendor’s destruction certificates lacked proof of tamper seals, and the clinic had no way to verify which media had been wiped.
Lessons Learned:
- Inspect seals and require on-site shredding witnesses
- Match certificate serial numbers to the actual media
- Centralize digital logs in a secure repository
They now insist on witness-led destruction and store every chain-of-custody record in one place.
Vendor Verification And Documentation
Before you sign on the dotted line, dig into credentials. A reliable vendor should have:
- ISO or R2 recycling certification and DoD wiping approval
- Valid state and federal disposal permits plus insurance
- Recent third-party compliance audits or client references
A rock-solid chain-of-custody log puts disputes to rest by recording every step of destruction.
Whether you’re shredding drives here or shipping them off-site, secure transport is non-negotiable.
E-Waste Recycling And Environmental Safety
Discarding hardware isn’t just about privacy; it’s about protecting soil and water too. Here’s how common methods stack up:
| Method | Devices | Benefits | Considerations |
|---|---|---|---|
| Physical Shredding | Hard drives, tapes | Irrecoverable destruction | Higher infrastructure costs |
| DoD Wipe | HDDs, SSDs | Allows safe hardware reuse | Must verify zero residual data |
| Certified Recycling | Computers, servers, cables | Meets environmental mandates | Complex sorting and logistics |
No matter the approach, record the endpoint for each device.
Three Essential Disposal Steps:
- Schedule on-site removal or drop-off at a certified center
- Obtain a destruction certificate listing serial numbers and methods
- Archive the certificate for your compliance audit trail
Afterward, your vendor provides a tamper-evident certificate confirming secure destruction. For a deeper dive on handling hardware and data disposal, check out our IT Asset Destruction Guide.
Audit Trail And Compliance
Defensible destruction isn’t just buzz—it’s proof you can show regulators at a moment’s notice.
Best Practices Include:
- Retain destruction logs according to your policy
- Link each certificate to the corresponding record ID
- Conduct annual audits of destruction reports and vendor compliance
Proper disposal protects your data and the planet in one sweep.
Metro Atlanta organizations should also follow Georgia EPD guidelines for e-waste recycling. Electronics often contain lead, mercury and cadmium—substances that demand specialized processing:
- Lead can leach into soil
- Mercury vaporizes when incinerated
- Cadmium contaminates waterways
- Plastics release dioxins if burned
Certified recyclers like Montclair Crew neutralize these hazards and recover valuable materials.
Final Verification Steps
Once destruction is complete, close the loop with a final check:
- Verify timestamps on destruction certificates
- Confirm custodian signatures on each form
- Update your retention schedule with disposal dates
- Notify stakeholders when the process wraps up
These last checks guarantee your disposal stands up to scrutiny and keeps your records retention policy defensible.
Sample Retention Schedule And Roll Out Checklist
Think of a retention schedule as a pulse-check for your records. It keeps you ahead in compliance and trims storage bills.
This template maps out who owns each file, how long to keep it, and when to circle back for a review.
Retention Schedule Template
First, sketch out your main record categories and custodians in the grid below. Slot in the retention period and the next review date. When regulations shift, simply update the calendar.
| Record Category | Retention Window | Custodian | Review Date |
|---|---|---|---|
| Administrative | 3 years | Office Manager | Jan 2025 |
| HR Records | 7 years | HR Director | Jul 2025 |
| Financial | 7 years | Finance Manager | Dec 2025 |
| Legal | 10 years | Legal Counsel | Mar 2026 |
Common Pitfalls
• Missing disposal receipts can void your audit defensibility
• Overlooked review dates often lead to noncompliance fines
Roll Out Checklist
Break your policy launch into four stages to ensure nothing slips through.
-
Policy Approval
Secure sign-off from Legal, Compliance, and Executive sponsors. -
Employee Training
Run bite-sized workshops and hand out quick-reference cards by role. -
System Configuration
Tag files in your document management tool for review alerts and deletion flags. -
Vendor Engagement
Lock in certified destruction and e-waste partners, then finalize SLAs.
Timely Reminder
Audit your process annually to catch gaps and confirm disposal logs.
Annual Audit Tips
Turn your yearly audit into a smooth check-in:
• Block time on the calendar for a full policy review
• Match disposal certificates against retention dates
• Have custodians perform random spot checks
• Log exceptions immediately and update the manual
Starting strong with these steps ensures your team nails record-retention from planning through enforcement.
Case Study Example
A Marietta retail chain put this template to work—and saw results in six months:
• Slashed archive space by 40%
• Achieved 100% disposal certificate coverage
• Eliminated missed review dates with clear role assignments
“This checklist was critical to meeting our audit deadline,” recalls the Records Manager.
Atlanta Disposal Partner
For secure destruction and e-waste disposal, partner with Montclair Crew Recycling:
• Free DoD three-pass hard drive wiping on-site
• Certified shredding for physical media and tapes
• Full chain-of-custody documentation and tamper-evident certificates
• Drop-off center in Smyrna plus service across Metro Atlanta
Weave these services into your rollout plan to streamline destruction and lock down compliance.
Yearly Review Checklist
- Legal Update
Scan for federal, state, and local law changes. - Stakeholder Meeting
Gather feedback from department heads and custodians. - Policy Revision
Revise and republish your manual. - Training Refresher
Run quick catch-up sessions for staff. - Reporting
Compile a summary of audit results and disposal metrics.
Completing this list keeps your schedule current, defensible, and ready for whatever comes next.
Record Retention Guidelines FAQ
Minimum Retention Period For Tax Documents
When it comes to tax paperwork, most companies hang on to returns and backup files for seven years. That mirrors the IRS’s audit window, giving you the breathing room to address any discrepancies or fraud investigations.
Managing Digital Vs. Physical Files
Handling electronic records and paper documents is like juggling two balls. Digital files come with automatic tags and timestamp logs, while physical files belong in locked cabinets. Yet both need the same clear-cut schedule if you want to stay audit-ready.
Key Management Tips
- Label every record with creation and deletion dates so nothing slips through the cracks.
- Use metadata tags or color-coded folders to flag items nearing their end-of-life.
- Scan paper documents into secure systems, then shred or recycle the originals.
“Consistent labeling across formats is the secret to seamless audits.” — Records Manager, SMB case study
Common Questions And Answers
What Are The Steps For Verifiable Destruction?
To wipe data beyond recovery, start by hiring a certified vendor and logging the chain-of-custody. Next, inspect tamper-evident certificates that list serial numbers. Finally, archive those destruction logs for future audits.
When Should We Review Our Policy?
A good rule is to revisit retention guidelines every 12 months or whenever regulations shift. Automated alerts can ping record owners when it’s time to circle back.
Numbered steps for a policy review:
- Gather custodians and legal advisors to outline needed changes.
- Update retention clocks and note any new statutes.
- Publish revisions and train your team on the updates.
Handling legal holds is a different beast. Pause destruction workflows and clearly flag each held record:
- Log the hold reason, start date, and responsible custodian.
- Notify every team involved to avoid accidental deletions.
This FAQ should cover your top record-retention concerns. For sample schedules or secure-destruction checklists, flip back to our earlier sections or templates.
Ready to lock down your data lifecycle and stay compliant? Partner with Montclair Crew Recycling.
