When we talk about electronic waste recycling, what we're really talking about is pulling valuable materials out of old, discarded electronics so we can make new products. It’s a smart process that keeps hazardous materials out of our environment and cuts down on the need for destructive mining.
The Hidden Problem in Your Old Devices

That old smartphone sitting in your desk drawer? The pile of obsolete laptops collecting dust in the office storage room? They might seem harmless, but they’re part of a massive, and rapidly growing, global problem. Every time a new gadget hits the market, an older one gets pushed out, adding to an enormous stream of what we call e-waste.
And this isn't just about a few old phones. E-waste is a catch-all for pretty much anything with a circuit board or a power cord.
- Corporate IT Assets: Think servers, computers, networking equipment, and printers.
- Business Equipment: Point-of-sale systems, specialized medical devices, and all kinds of telecommunications hardware.
- Everyday Electronics: Old TVs, kitchen appliances, and even your kids' electric toys.
The Alarming Scale of Electronic Waste
The sheer volume of electronics we're tossing aside is staggering. Globally, e-waste is piling up five times faster than we can formally recycle it. In 2022 alone, the world generated a mind-boggling 62 million metric tons of e-waste—that's an 82% increase from 2010.
To give you a sense of that scale, that much weight would fill 1.55 million 40-ton trucks. If you lined them all up, they would wrap around the entire equator.
This is why getting a handle on electronic waste recycling has become so urgent. It's more than just an environmental headache; it’s a critical issue for any business. Every device we discard is a complex mix of both valuable resources and hazardous materials. If handled improperly, those toxic components can do serious damage. You can learn more about the environmental impact of electronic waste in our detailed guide.
When we toss out old electronics, we're not just creating trash. We are discarding valuable resources like gold, copper, and palladium, while simultaneously creating a toxic legacy of lead and mercury for future generations.
This is why having a clear plan for your old technology is no longer optional. Proper recycling is the only way to safely get that value back while preventing an environmental crisis from getting worse. The story of your old equipment is part of a much bigger, global narrative.
Understanding the Electronic Waste Recycling Process
So, what exactly is electronic waste recycling? Let's skip the dry, textbook definition. A better way to think about it is as a modern-day treasure hunt—a kind of urban mining where old server rooms and forgotten storage closets are the new gold mines.
This whole process is a calculated mission to reclaim the valuable materials locked inside our old electronics. Your company's retired servers, laptops, and networking gear are packed with gold, silver, copper, and palladium. By carefully pulling these resources out, we can feed them back into the manufacturing stream for new products. This dramatically cuts our dependence on destructive, environmentally-costly traditional mining.
It’s a smart approach that turns what could be a major liability into a real asset for a circular economy.
Certified Recycling vs Improper Disposal
It's absolutely critical to understand that not all "recycling" is created equal. Just dropping off your old equipment at a generic collection event doesn't mean it's being handled responsibly. Improper disposal, like letting e-waste end up in a landfill, is an environmental disaster in the making.
When electronics are dumped, hazardous materials like lead and mercury can seep into the soil and groundwater, causing contamination for generations. This lazy approach gives you zero value recovery and opens your business up to serious compliance risks.
True electronic waste recycling isn’t just about getting rid of old gear. It's a proactive strategy for conserving resources and preventing pollution. It’s about intelligently recovering value while shielding your business and the environment from harm.
On the flip side, certified recycling is a secure, transparent, and professional process. When you partner with qualified electronic waste companies, you get a guarantee that every single device is managed according to strict environmental and data security standards. This is the only path that ensures hazardous components are safely neutralized and valuable materials make their way back into the supply chain.
Improper Disposal vs Certified Recycling
To really see the difference, let’s put the two methods side-by-side. The choice becomes pretty clear.
| Action | Improper Disposal (Landfill/Incineration) | Certified Recycling (Responsible Partner) |
|---|---|---|
| Environmental Impact | Releases toxic chemicals into soil, water, and air, causing long-term pollution. | Prevents pollution by safely containing and processing hazardous materials. |
| Resource Management | Wastes valuable and finite materials like gold, copper, and rare earth metals. | Recovers precious materials, reducing the need for new mining and conserving natural resources. |
| Data Security | Leaves sensitive corporate and customer data vulnerable to theft and breaches. | Guarantees complete data destruction through certified wiping or physical shredding. |
| Business Value | Creates potential legal liabilities and offers zero financial return. | Recovers financial value from retired assets and ensures full regulatory compliance. |
In the end, choosing certified electronic waste recycling isn't a cost—it's an investment in security, sustainability, and smart business. It’s the only way to make sure your retired technology becomes part of a positive future instead of a toxic problem.
The Risks Lurking in Your Discarded Tech
Those old electronics collecting dust in a storage closet aren't just taking up space. Think of them as tiny, ticking time bombs for both the environment and your company's data security. Once tossed into a landfill, that obsolete server or old monitor starts to break down, leaching a nasty cocktail of toxic substances directly into the ecosystem.
So, what's really inside a typical office computer? The circuit boards are often packed with lead, a powerful neurotoxin. Old-school CRT monitors and even some flat-screen displays can contain mercury and cadmium—heavy metals notorious for causing severe health problems. When these devices are left to rot in a landfill, rain washes these toxins into the soil, which can contaminate the groundwater that local communities depend on. Burn them, and you're just releasing those same harmful pollutants into the air we all breathe.
Environmental Hazards in Common Devices
The scale of this problem is hard to wrap your head around. In 2021 alone, the world generated an estimated 57.4 million metric tons of electronic waste. The truly shocking part? A staggering 82.6% of it wasn't properly collected and recycled. That means millions of tons of hazardous materials were simply dumped, posing a serious threat to our planet and our health.
Here's a quick look at the main offenders:
- Lead: Found in the glass of old CRT monitors and the solder on circuit boards. It can severely damage the nervous system, kidneys, and reproductive systems.
- Mercury: A key component in the fluorescent lamps inside flat-screen displays. It's known to cause significant brain and kidney damage.
- Cadmium: Commonly used in rechargeable computer batteries and semiconductors. It's a known carcinogen.
The Critical Business Risk of a Data Breach
Beyond the environmental mess, there's a more immediate and painful threat to your business: data breaches. Every single discarded hard drive, server, or company phone is a potential treasure chest for cybercriminals. Simply deleting files or hitting "factory reset" just doesn't cut it. That data is still there, waiting to be found.
An improperly discarded hard drive is like leaving your company's filing cabinet unlocked on a public street. Financial records, customer lists, and proprietary information are all left completely exposed and vulnerable to theft.
It’s surprisingly easy for someone with the right tools to recover "deleted" files from a hard drive that hasn't been professionally wiped clean. This kind of oversight can lead to a world of hurt, including massive regulatory fines, crippling financial losses, and irreversible damage to your brand's reputation.
This is exactly why professional data destruction isn't just a good idea—it's a non-negotiable part of any IT asset disposal plan. To truly protect your business, you need to understand what data sanitization is and how it permanently nukes sensitive information. Getting a handle on e-waste recycling is just as much about locking down your data as it is about protecting the environment.
From Your Doorstep to New Materials
Ever wonder what actually happens to your old electronics after they leave your office? It’s not a simple trip to the local dump. Think of it as the start of a new life—a highly detailed process of deconstruction and rebirth that turns obsolete gear into the raw materials for tomorrow's technology.
The journey starts with a secure pickup and transport. This first step is absolutely critical for maintaining a clear chain of custody, ensuring every single piece of equipment is tracked from the moment it leaves your facility. For businesses in the Atlanta area, scheduling a secure e-waste pickup is the easiest way to kick things off, guaranteeing your assets are handled by professionals from start to finish. Once the truck arrives at a certified facility, the real work begins.
Initial Sorting and Careful Dismantling
Inside the recycling plant, the first thing that happens is manual sorting. Trained technicians sift through the incoming stream of devices, separating laptops from servers and monitors from old networking gear. This ensures that different types of equipment and the materials they contain are channeled into the correct processing streams right from the get-go.
After the initial sort, items are carefully taken apart by hand. This isn't just for efficiency; it's a critical safety measure. Technicians methodically remove any hazardous components that need special handling, such as:
- Batteries: Lithium-ion and other batteries are pulled out first to prevent fire hazards and ensure they are recycled in a separate, specialized process.
- Ink and Toner Cartridges: These are separated to avoid messy spills and to properly process the plastic and leftover ink.
- Mercury-Containing Components: Things like the small fluorescent lamps found in older flat-screen monitors are carefully extracted and isolated.
This manual deconstruction is essential. It gets dangerous materials out of the way before the devices head to the big machinery, protecting both the workers and the environment.
Securing Data and Separating Materials
With the hazardous stuff removed, the next priority is data destruction. For any business, this is a non-negotiable step. To make sure your information is gone for good, hard drives and other storage media are physically shredded into tiny, confetti-like pieces. This physical destruction gives you absolute certainty that sensitive company or customer data can never be recovered or compromised.
The infographic below really drives home the dual risks you face with improper disposal: environmental harm and data theft.
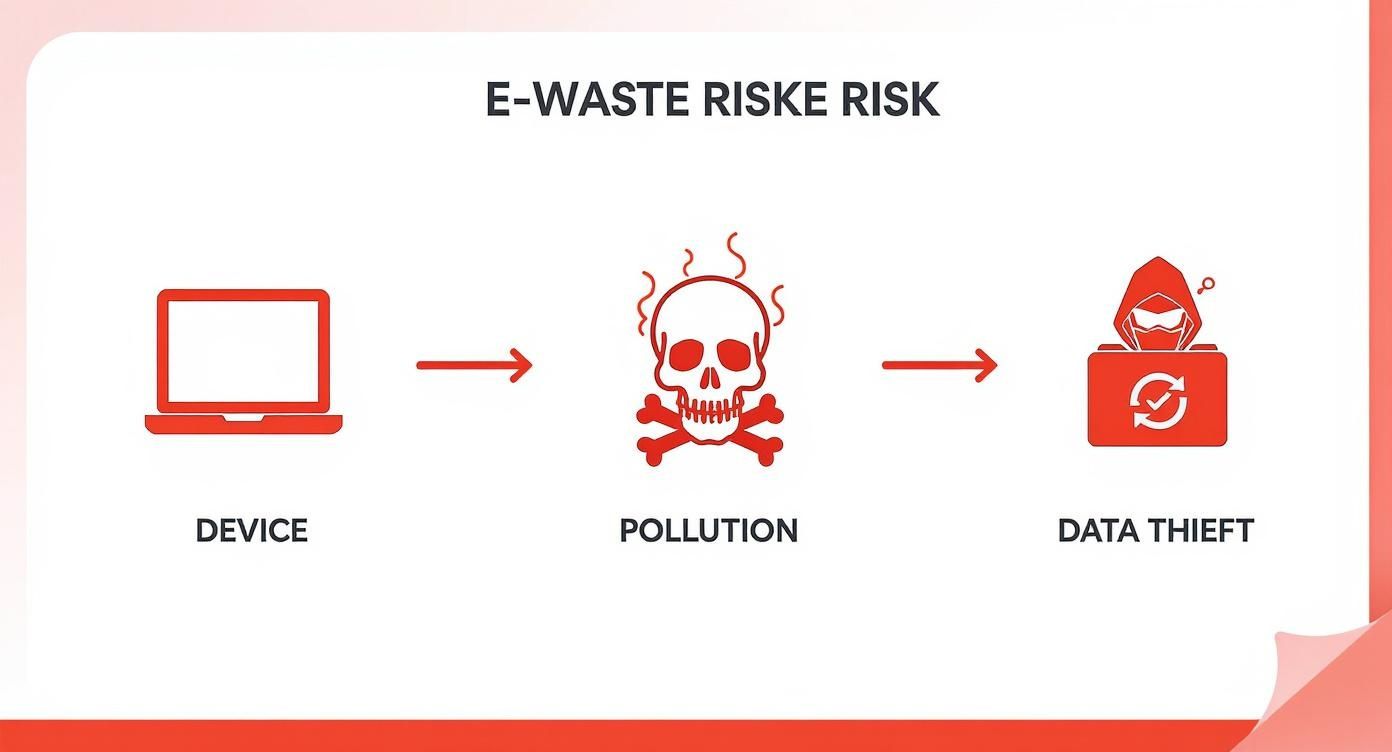
It’s a clear visual reminder of how a single old device can create two very different, but equally damaging, problems if it isn't handled by certified pros.
After the data is destroyed, what's left moves into the final, high-tech phase: mechanical separation. The shredded fragments are dumped onto conveyor belts that run through a series of advanced sorting machines.
Mechanical separation is like an automated treasure hunt. Powerful overhead magnets snatch up iron-based metals like steel, while special machines generating eddy currents repel non-ferrous metals like aluminum and copper, pushing them into separate collection bins.
Finally, advanced optical sorters might use infrared beams to identify and separate the different kinds of plastics. What you're left with is a collection of clean, sorted raw materials—metals, plastics, and glass—ready to be sold back to manufacturers. These commodities are then used to build brand new products, closing the loop and turning your old IT assets into valuable resources for a circular economy.
Turning Obsolete Technology into Real Value
Those old electronics gathering dust in a storage closet aren't just a disposal headache—they're a strategic opportunity waiting to be unlocked. It’s a concept experts call the "urban mine," a massive, untapped reservoir of valuable materials hiding in plain sight within our retired technology.
Instead of seeing old IT assets as liabilities that cost money to get rid of, smart businesses are starting to see them for what they really are: a source of recoverable value.
Think about it. Every server, laptop, and smartphone is packed with a complex mix of precious and industrial metals. Gold and silver get all the attention, but these devices are also loaded with copper, aluminum, and rare earth elements. These are the exact same materials needed to manufacture everything from new computers to the next generation of electric vehicles.
Recovering Value from Your IT Assets
So, how do you tap into this hidden value? You partner with a certified IT Asset Disposition (ITAD) provider. This is the move that transforms recycling from a simple compliance chore into a genuine revenue-generating activity.
A professional partner doesn’t just haul your equipment away. They meticulously assess its potential for resale, refurbishment, or harvesting valuable components. In fact, before even thinking about recycling, it’s worth exploring options like extending the life of your iPhone through repair and refurbishment to squeeze every last drop of value out of a device.
A professional ITAD program is not a cost center. It's an investment in security, sustainability, and financial recovery, turning outdated equipment into a tangible return for your business.
The scale of this opportunity is staggering. In 2022 alone, the metals trapped inside the world's e-waste were valued at an estimated $91 billion. But only a tiny fraction of that value was ever actually recovered, which points to a massive missed economic opportunity for businesses everywhere.
Strengthening Your Brand and ESG Goals
Beyond the direct financial return, a responsible e-waste recycling program gives a company’s brand reputation a serious boost. Today’s consumers, partners, and investors are laser-focused on Environmental, Social, and Governance (ESG) criteria. A transparent, certified recycling program is proof of a real commitment to sustainability.
This doesn't just polish your brand image. It helps attract and retain top talent, because people want to work for companies that align with their own values. Suddenly, what started as a conversation about electronic waste recycling becomes a powerful tool for building a more resilient, respected, and forward-thinking organization.
Common E-Waste Recycling Questions
So, you understand the why behind e-waste recycling, but the practical side of things can still feel a bit murky. When businesses decide to get serious about a responsible electronics program, a few key questions always pop up. Let's clear the air and tackle those common concerns head-on.
What Types of Electronics Can Be Recycled?
You’d be surprised. The list of what can be recycled goes way beyond the obvious stuff like old computers, laptops, printers, and monitors. Think bigger.
We’re talking about all the networking gear that keeps your business online—routers, switches, servers, and telecommunications equipment. It also includes mobile phones, tablets, and even the smaller things like keyboards and mice. The simple rule is this: if it has a circuit board or a power cord, a certified facility can process it. From massive data center hardware down to the smallest office gadget, it all has a place in the recycling stream.
Is E-Waste Recycling Expensive for a Business?
It’s easy to see recycling as just another line-item expense, but it’s smarter to view it as an investment in risk management. A single data breach or a fine for improper disposal can cost your business multiples of what you would have spent on professional recycling. The math is simple.
The question isn't whether you can afford to recycle your e-waste, but whether you can afford not to. The hidden costs of improper disposal—from data breaches to environmental fines—are far greater than the price of certified recycling.
Plus, many of your retired IT assets still have life left in them, and that means they still have value. Through IT Asset Disposition (ITAD) services, you can often offset or completely cover your recycling costs. In some cases, you can even turn a profit by remarketing usable components and recovering valuable materials like copper and gold. A transparent partner will always work to get you the maximum return.
How Can I Guarantee My Data Is Securely Destroyed?
This is the big one. Data security is non-negotiable, and it’s the most critical piece of this whole puzzle. Any certified e-waste recycler worth their salt uses verifiable and auditable methods to make sure your sensitive information is gone for good.
There are two main ways to get this done:
- Physical Destruction: This is the most direct and foolproof method. Hard drives and other storage devices are run through industrial shredders that chew them up into tiny, confetti-like pieces. At that point, getting any data back is physically impossible.
- Secure Data Wiping: For drives that might be reused or remarketed, we use specialized software to overwrite the data again and again. This process follows strict government and industry standards, like the NIST 800-88 guidelines, to ensure the original information is permanently erased.
Even before sending your devices off, it's a good practice to perform a software wipe yourself. Our guide on how to wipe a computer before recycling walks you through the essential steps. Once a certified vendor finishes the job, they must provide you with a Certificate of Destruction. This is your legal proof that the data has been eliminated, protecting you from any future liability.
What Do R2 and e-Stewards Certifications Mean?
When you see logos for R2 (Responsible Recycling) or e-Stewards, you're looking at a seal of approval. These aren't just fancy badges; they are hard-won credentials from independent, third-party auditors. A facility only earns them after proving it can meet and maintain the industry's highest standards through rigorous, ongoing audits.
These certifications guarantee that a recycler follows strict rules for:
- Environmental Safety: Preventing hazardous materials from being illegally exported or dumped in local landfills.
- Data Security: Using documented, airtight procedures for destroying data.
- Worker Health and Safety: Protecting their team from exposure to harmful materials.
Choosing a partner with an R2 or e-Stewards certification is the single best way to know your e-waste is being managed legally, securely, and responsibly. It takes all the guesswork out of the equation.
Ready to implement a secure, compliant, and value-driven e-waste recycling program for your Atlanta-area business? Montclair Crew Recycling provides certified ITAD services that protect your data and the environment. Contact us today for a free consultation.
